[LeetCode][114. Flatten Binary Tree to Linked List] 3 Approaches: PreOrder, Iteration and Recursion
By Long Luo
This article is the solution Image Explanation to Understand the Recursion Solution of Problem 114. Flatten Binary Tree to Linked List .
The Binary Tree Traversal Algorithms can be find here Tree Traversal Algorithms: PreOrder, InOrder and PostOrder .
We can use DFS to traversal the binary tree.
PreOrder + List
It’s easy to find that the flatten tree is the PreOrder of the tree. We can preorder the tree and store the TreeNodes in a List.
Traversal the list, make the current node as the preNode’s right node.1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25public void flatten(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
List<TreeNode> nodeList = new ArrayList<>();
preOrder(root, nodeList);
int n = nodeList.size();
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
TreeNode preNode = nodeList.get(i - 1);
TreeNode currNode = nodeList.get(i);
preNode.left = null;
preNode.right = currNode;
}
}
public void preOrder(TreeNode root, List<TreeNode> nodeList) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
nodeList.add(root);
preOrder(root.left, nodeList);
preOrder(root.right, nodeList);
}
We can also traversal the tree iteratively with a Stack:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26public void flatten(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
List<TreeNode> nodeList = new ArrayList<>();
Stack<TreeNode> stk = new Stack<>();
while (root != null || !stk.empty()) {
while (root != null) {
nodeList.add(root);
stk.push(root);
root = root.left;
}
root = stk.pop();
root = root.right;
}
int len = nodeList.size();
for (int i = 1; i < len; i++) {
TreeNode preNode = nodeList.get(i - 1);
TreeNode currNode = nodeList.get(i);
preNode.left = null;
preNode.right = currNode;
}
}
Analysis
- Time Complexity: \(O(n)\).
- Space Complexity: \(O(n)\).
Iteration
The Process is as follows:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49 1
/ \
2 5
/ \ \
3 4 6
// 1. Insert the left subtree of 1 to the right subtree
1
\
2 5
/ \ \
3 4 6
// 2. Let the right subtree to the right node of the farest right node of the left subtree.
1
\
2
/ \
3 4
\
5
\
6
//3. Insert the left subtree of 2 to the right subtree
1
\
2
\
3 4
\
5
\
6
// 4. Let the original right subtree to the right node of the farest right node of the left subtree.
1
\
2
\
3
\
4
\
5
\
6
......
Let’s coding it.1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17public void flatten(TreeNode root) {
while (root != null) {
if (root.left == null) {
root = root.right;
} else {
TreeNode pre = root.left;
while (pre.right != null) {
pre = pre.right;
}
pre.right = root.right;
root.right = root.left;
root.left = null;
root = root.right;
}
}
}
Analysis
- Time Complexity: \(O(n)\)
- Space Complexity: \(O(n)\)
Recursion
To Flatten Binary Tree to Linked List, there are 3 steps as the picture shows.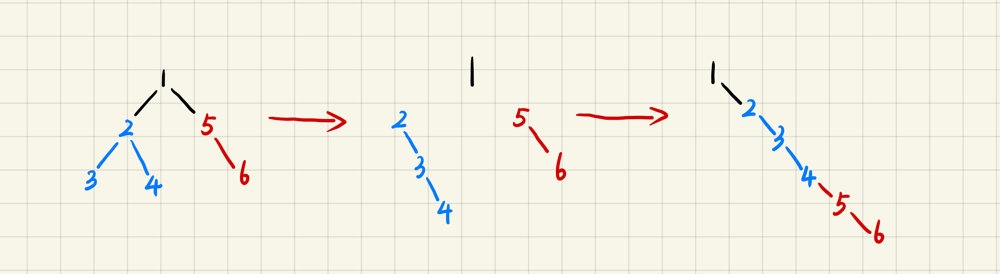
- Flatten the left subtree of the root node into a linked list;
- Flatten the right subtree of the root node into a linked list;
- Let the right subtree of the step 2 be the right child of the farest right node of the left subtree of step 1.
Obiously, that’s a recursion process.
Let’s coding it.1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21 public static void flatten_rec(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
// left subtree
flatten_rec(root.left);
// right subtree
flatten_rec(root.right);
TreeNode temp = root.right;
root.right = root.left;
root.left = null;
// find the farest right node.
while (root.right != null) {
root = root.right;
}
root.right = temp;
}
Analysis
- Time Complexity: \(O(n)\).
- Space Complexity: \(O(n)\).
References:
All suggestions are welcome. If you have any query or suggestion please comment below. Please upvote👍 if you like💗 it. Thank you:-)
Explore More Leetcode Solutions. 😉😃💗