[LeetCode][329. Longest Increasing Path in a Matrix] 4 Approaches: BFS, Memorization DFS, DP, Topo Sorting
By Long Luo
This article is the solution 4 Approaches: BFS, Memorization DFS, DP, Topo Sorting of Problem 329. Longest Increasing Path in a Matrix.
Here shows 4 Approaches to slove this problem: BFS, Memorization DFS, DP, Topological Sorting.
BFS
The simplest method that comes to my mind is BFS. We start search from each node, spread out like water, to see how far it can flood, and record the maximum flood path length of all nodes.1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59class Solution {
public int longestIncreasingPath(int[][] matrix) {
if (matrix == null || matrix.length == 0 || matrix[0].length == 0) {
return 0;
}
int row = matrix.length;
int col = matrix[0].length;
if (row == 1 && col == 1) {
return 1;
}
int max = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < row; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < col; j++) {
max = Math.max(max, bfs(matrix, i, j));
}
}
return max;
}
public int bfs(int[][] matrix, int x, int y) {
int[][] dirs = {{-1, 0}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}, {0, 1}};
int ans = 0;
int row = matrix.length;
int col = matrix[0].length;
Queue<int[]> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(new int[]{x, y});
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int size = queue.size();
ans++;
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
int[] curPos = queue.poll();
for (int[] dir : dirs) {
int nextX = curPos[0] + dir[0];
int nextY = curPos[1] + dir[1];
if (nextX < 0 || nextX >= row || nextY < 0 || nextY >= col) {
continue;
}
if (matrix[nextX][nextY] <= matrix[curPos[0]][curPos[1]]) {
continue;
}
queue.offer(new int[]{nextX, nextY});
}
}
}
return ans;
}
}
Analysis
- Time Complexity: \(O(m^2n^2)\).
- Space Complexity: \(O(mn)\).
Memory + DFS
It’s easy to figure out that there are some repeated enqueuing in BFS method.
Take a example, when searching the longest path of \(2\), the longest path of \(6\) will also be searched. However, we will search \(6\) again as a starting node in BFS.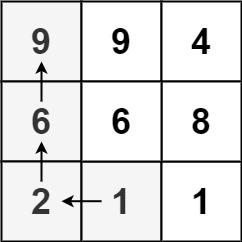
So how to prune the search?
If we search \(6\) first and store the result. When search \(2\), we can know the result is \(len(2) + len(6)\).
So we can use a memory to store the result, use DFS to search the longest path of each node.1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53class Solution {
public int longestIncreasingPath(int[][] matrix) {
int row = matrix.length;
int col = matrix[0].length;
if (row == 1 && col == 1) {
return 1;
}
int max = 0;
int[][] memo = new int[row][col];
for (int i = 0; i < row; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < col; j++) {
if (memo[i][j] == 0) {
max = Math.max(max, dfs(matrix, memo, i, j));
}
}
}
return max;
}
public int dfs(int[][] matrix, int[][] memo, int x, int y) {
if (memo[x][y] > 0) {
return memo[x][y];
}
int[][] dirs = {{-1, 0}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}, {0, 1}};
int ans = 1;
int row = matrix.length;
int col = matrix[0].length;
for (int[] dir : dirs) {
int nextX = x + dir[0];
int nextY = y + dir[1];
if (nextX < 0 || nextX >= row || nextY < 0 || nextY >= col) {
continue;
}
if (matrix[nextX][nextY] <= matrix[x][y]) {
continue;
}
ans = Math.max(ans, dfs(matrix, memo, nextX, nextY) + 1);
}
memo[x][y] = ans;
return ans;
}
}
Analysis
- Time Complexity: \(O(mn)\).
- Space Complexity: \(O(mn)\).
DP
We can also use the DP to solve this problem.
\(dp[i][j]\) means the longest path from the position of \(matrix[i][j]\).
The DP tranfer equation is as follows:
\[ dp[i][j] = max(dp[i][j], dp[nextX][nextY] + 1), matrix[nextX][nextY] > matrix[i][j] \]
- At the beginning, all the node is \(1\).
- We should search the larger adjacent nodes first.
1 | class Solution { |
Analysis
- Time Complexity: \(O(mnlog(mn)\).
- Space Complexity: \(O(mn)\).
Topo Sorting
Consider the matrix as a directed graph, and calculate the out-degree corresponding to each cell, how many edges start from the cell.
If the value of a cell is smaller than the value of all adjacent cells, so the out-degree of the cell will increate.
We can solve this problem using topo sorting.1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66class Solution {
public int longestIncreasingPath(int[][] matrix) {
int row = matrix.length;
int col = matrix[0].length;
if (row == 1 && col == 1) {
return 1;
}
int[][] dirs = {{-1, 0}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}, {0, 1}};
int[][] outDegrees = new int[row][col];
for (int i = 0; i < row; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < col; j++) {
for (int[] dir : dirs) {
int nextX = i + dir[0];
int nextY = j + dir[1];
if (nextX < 0 || nextX >= row || nextY < 0 || nextY >= col || matrix[nextX][nextY] <= matrix[i][j]) {
continue;
}
outDegrees[i][j]++;
}
}
}
Queue<int[]> queue = new LinkedList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < row; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < col; j++) {
if (outDegrees[i][j] == 0) {
queue.offer(new int[]{i, j});
}
}
}
int max = 0;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
max++;
int size = queue.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
int[] curPos = queue.poll();
int x = curPos[0];
int y = curPos[1];
for (int[] dir : dirs) {
int prevX = x + dir[0];
int prevY = y + dir[1];
if (prevX < 0 || prevX >= row || prevY < 0 || prevY >= col) {
continue;
}
if (matrix[prevX][prevY] >= matrix[x][y]) {
continue;
}
if (--outDegrees[prevX][prevY] == 0) {
queue.offer(new int[]{prevX, prevY});
}
}
}
}
return max;
}
}
Analysis
- Time Complexity: \(O(mn)\).
- Space Complexity: \(O(mn)\).
All suggestions are welcome. If you have any query or suggestion please comment below. Please upvote👍 if you like💗 it. Thank you:-)
Explore More Leetcode Solutions. 😉😃💗