[LeetCode][114. Flatten Binary Tree to Linked List] 3 Approaches: PreOrder, Iteration and Recursion
By Long Luo
This article is the solution Image Explanation to Understand the Recursion Solution of Problem 114. Flatten Binary Tree to Linked List.
The Binary Tree Traversal Algorithms can be find here Tree Traversal Algorithms: PreOrder, InOrder and PostOrder.
We can use DFS to traversal the binary tree.
PreOrder + List
It’s easy to find that the flatten tree is the PreOrder of the tree. We can preorder the tree and store the TreeNodes in a List.
Traversal the list, make the current node as the preNode’s right node.1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25public void flatten(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
List<TreeNode> nodeList = new ArrayList<>();
preOrder(root, nodeList);
int n = nodeList.size();
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
TreeNode preNode = nodeList.get(i - 1);
TreeNode currNode = nodeList.get(i);
preNode.left = null;
preNode.right = currNode;
}
}
public void preOrder(TreeNode root, List<TreeNode> nodeList) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
nodeList.add(root);
preOrder(root.left, nodeList);
preOrder(root.right, nodeList);
}
We can also traversal the tree iteratively with a Stack:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26public void flatten(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
List<TreeNode> nodeList = new ArrayList<>();
Stack<TreeNode> stk = new Stack<>();
while (root != null || !stk.empty()) {
while (root != null) {
nodeList.add(root);
stk.push(root);
root = root.left;
}
root = stk.pop();
root = root.right;
}
int len = nodeList.size();
for (int i = 1; i < len; i++) {
TreeNode preNode = nodeList.get(i - 1);
TreeNode currNode = nodeList.get(i);
preNode.left = null;
preNode.right = currNode;
}
}
Analysis
- Time Complexity: \(O(n)\).
- Space Complexity: \(O(n)\).
Iteration
The Process is as follows:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49 1
/ \
2 5
/ \ \
3 4 6
// 1. Insert the left subtree of 1 to the right subtree
1
\
2 5
/ \ \
3 4 6
// 2. Let the right subtree to the right node of the farest right node of the left subtree.
1
\
2
/ \
3 4
\
5
\
6
//3. Insert the left subtree of 2 to the right subtree
1
\
2
\
3 4
\
5
\
6
// 4. Let the original right subtree to the right node of the farest right node of the left subtree.
1
\
2
\
3
\
4
\
5
\
6
......
Let’s coding it.1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17public void flatten(TreeNode root) {
while (root != null) {
if (root.left == null) {
root = root.right;
} else {
TreeNode pre = root.left;
while (pre.right != null) {
pre = pre.right;
}
pre.right = root.right;
root.right = root.left;
root.left = null;
root = root.right;
}
}
}
Analysis
- Time Complexity: \(O(n)\).
- Space Complexity: \(O(n)\).
Recursion
To Flatten Binary Tree to Linked List, there are 3 steps as the picture shows.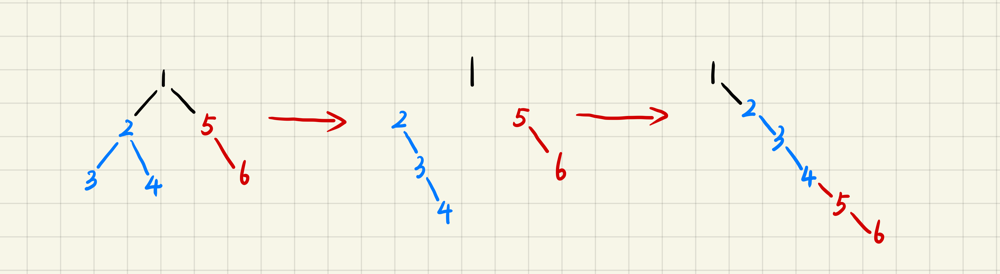
- Flatten the left subtree of the root node into a linked list;
- Flatten the right subtree of the root node into a linked list;
- Let the right subtree of the step 2 be the right child of the farest right node of the left subtree of step 1.
Obiously, that’s a recursion process.
Let’s coding it.1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21 public static void flatten_rec(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
// left subtree
flatten_rec(root.left);
// right subtree
flatten_rec(root.right);
TreeNode temp = root.right;
root.right = root.left;
root.left = null;
// find the farest right node.
while (root.right != null) {
root = root.right;
}
root.right = temp;
}
Analysis
- Time Complexity: \(O(n)\).
- Space Complexity: \(O(n)\).
References:
All suggestions are welcome. If you have any query or suggestion please comment below. Please upvote👍 if you like💗 it. Thank you:-)
Explore More Leetcode Solutions. 😉😃💗