[LeetCode][21. Merge Two Sorted Lists] The Recursive Algorithm with Detailed Image Explanation
By Long Luo
This article is the solution The Recursive Algorithm with Detailed Image Explanation of Problem 21. Merge Two Sorted Lists.
Intuition
We can use Recursion to solve this problem.
The key points of Recursion are \(2\).
How to terminate the recursion: Returns when either \(\texttt{l1}\) or \(\texttt{l2}\) is \(\texttt{null}\).
What to do in the process: if \(\texttt{l1.val} \le \texttt{l2.val}\), then point \(\texttt{l1.next}\) to the smaller of \(\texttt{l1}\) and \(\texttt{l2}\).
If \(\texttt{l1.val} \le \texttt{l2.val}\), we can choose the smaller node, such as \(\texttt{l1}\). However, the linked list is not reached the end, we will continue to compare.
Now we are compare \(\texttt{l1.next}\) and \(\texttt{l2}\). The \(\texttt{l1.next}\) and \(\texttt{l2}\) are processed in the recursive functions of the next layer.
We process such process and finally get the result.
Image Explanation
You can get a intuition from below images.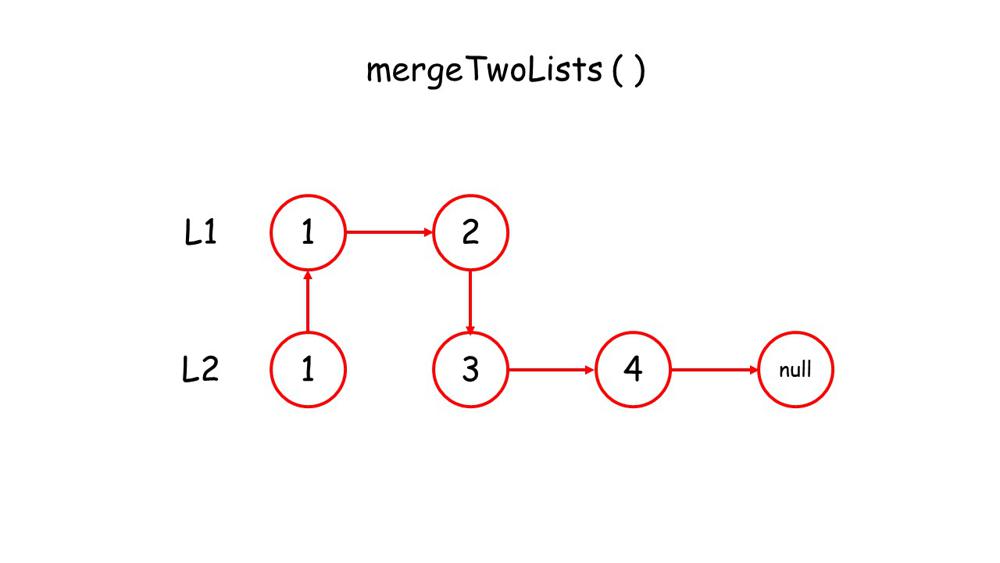
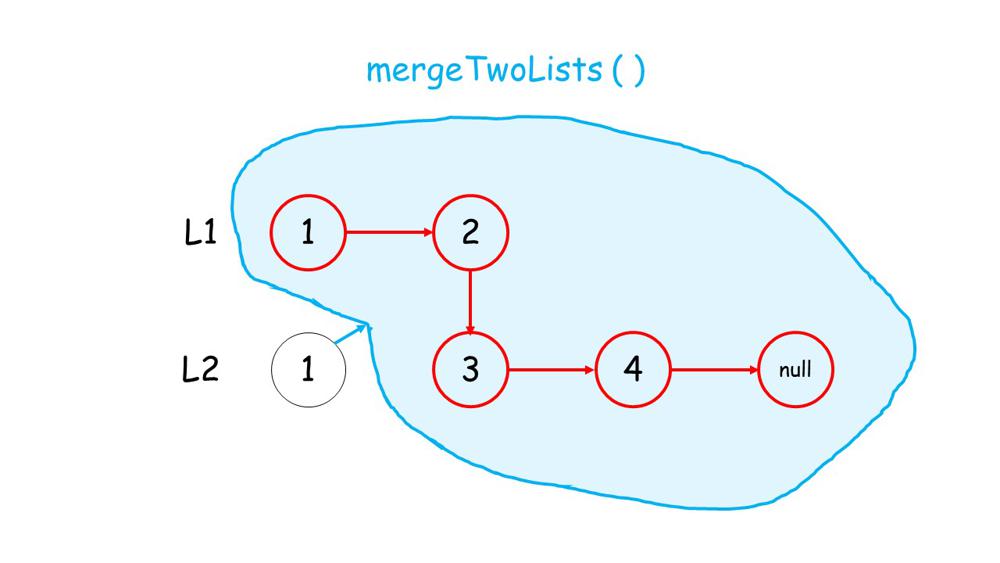
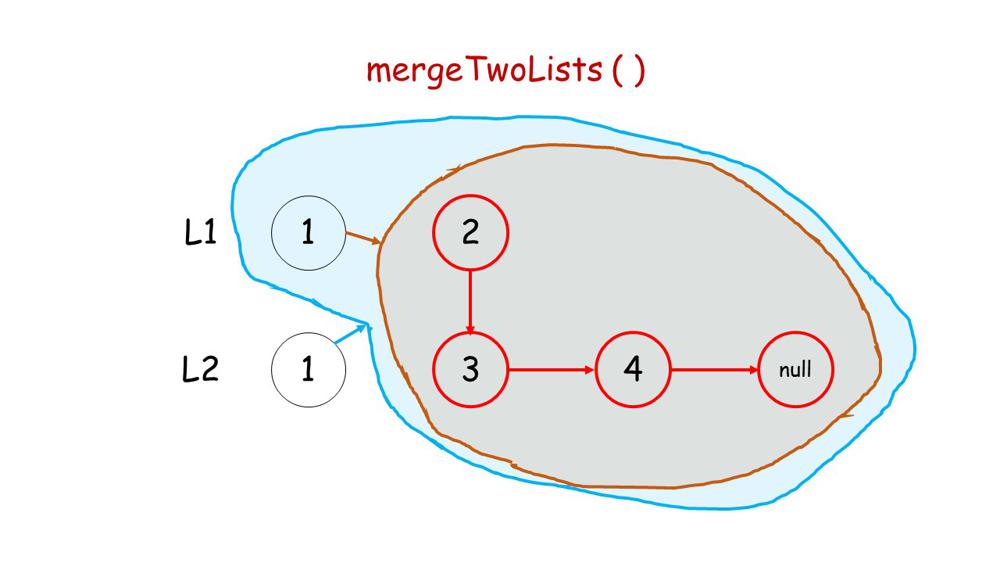
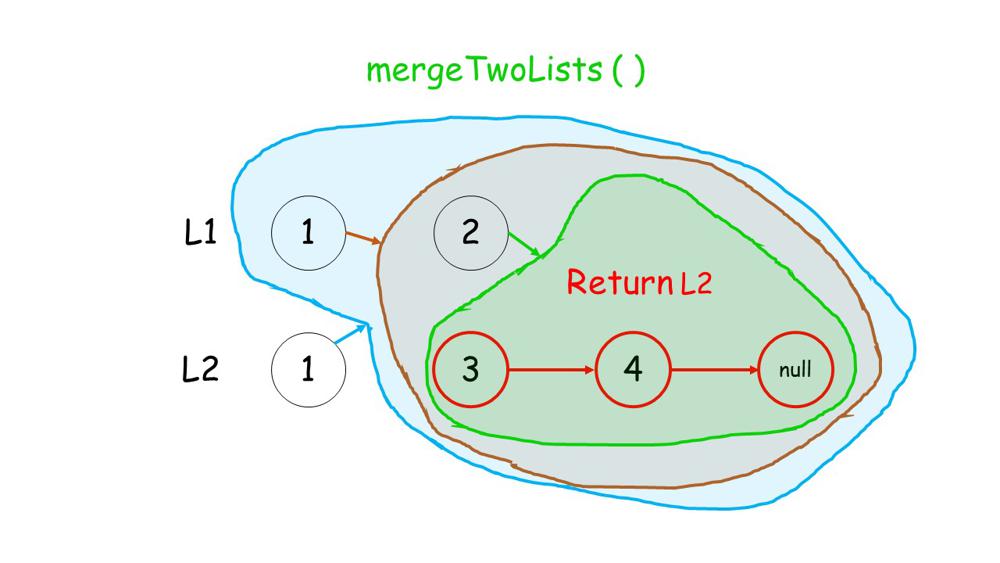
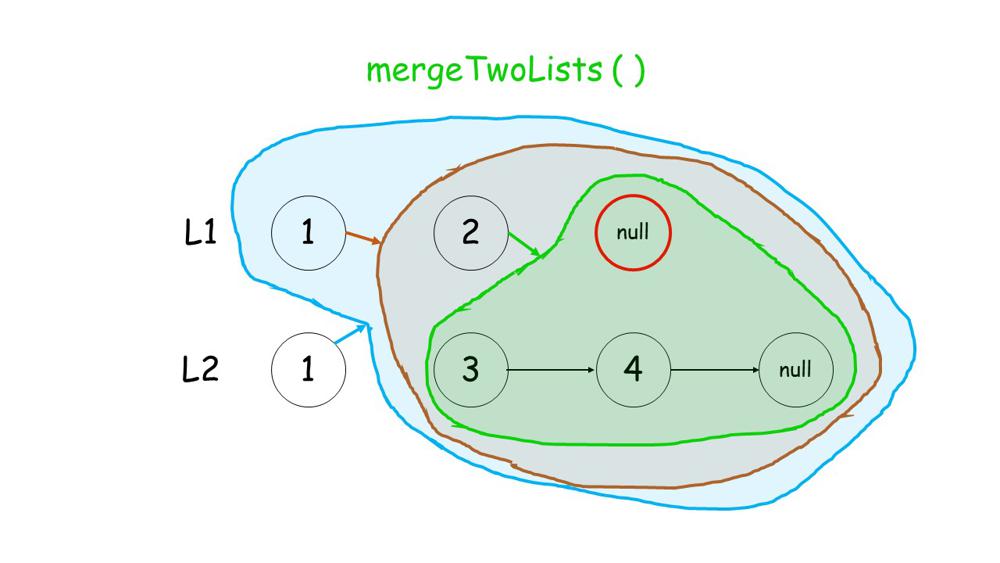
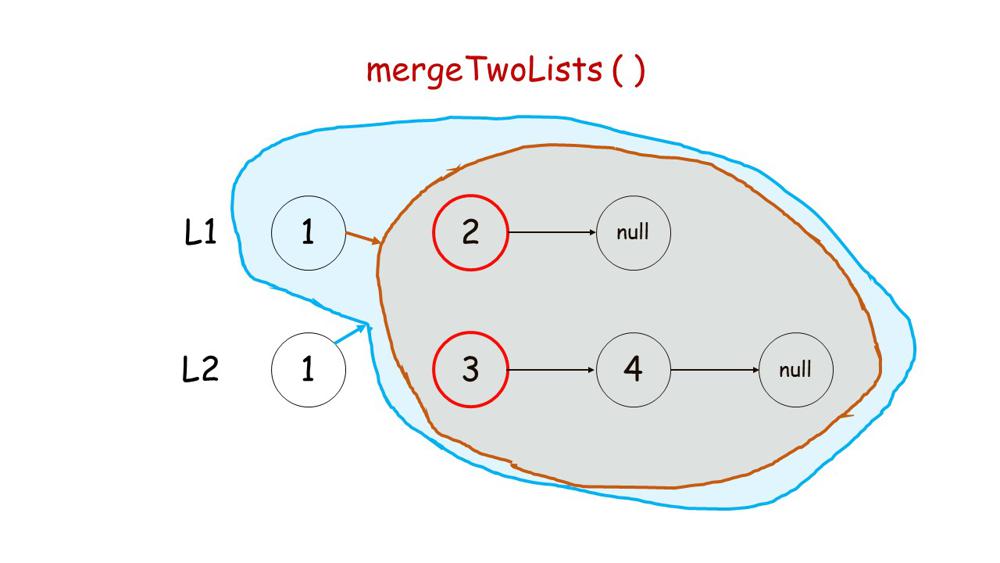
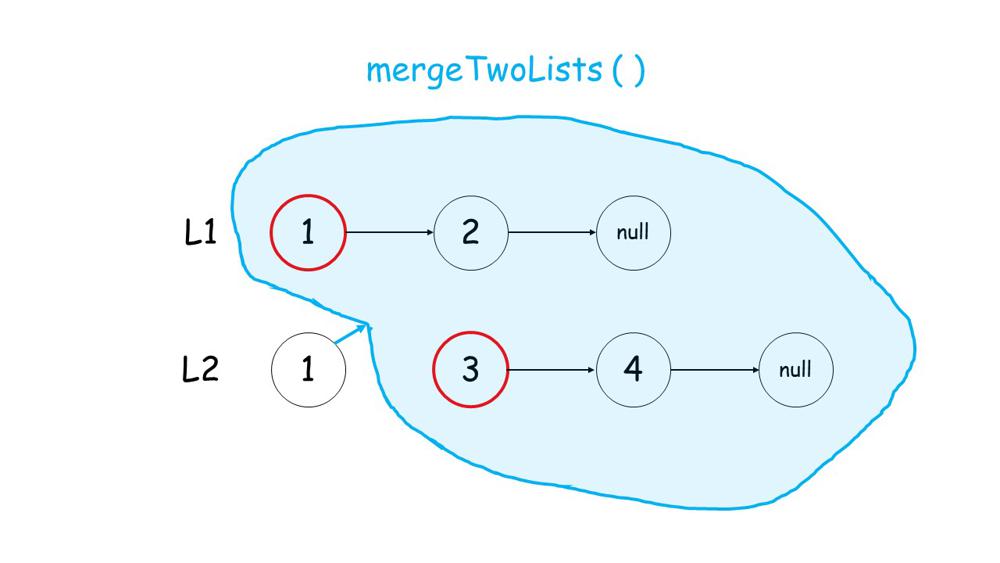
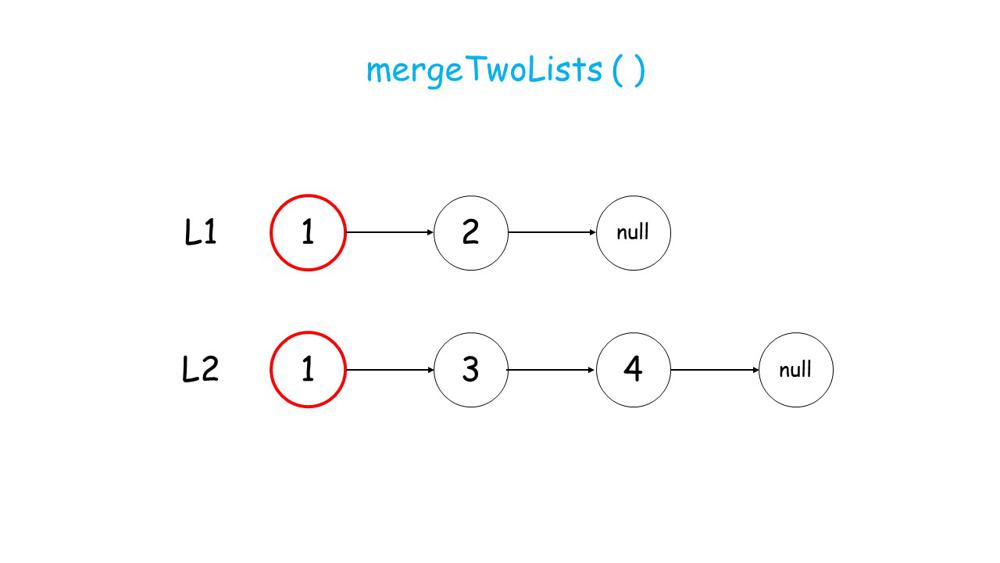
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15class Solution {
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
if (l1 == null) {
return l2;
} else if (l2 == null) {
return l1;
} else if (l1.val < l2.val) {
l1.next = mergeTwoLists(l1.next, l2);
return l1;
} else {
l2.next = mergeTwoLists(l1, l2.next);
return l2;
}
}
}
Analysis
- Time Complexity: \(O(m + n)\).
- Space Complexity: \(O(m + n)\).
All suggestions are welcome. If you have any query or suggestion please comment below. Please upvote👍 if you like💗 it. Thank you:-)
Explore More Leetcode Solutions. 😉😃💗