[Leetcode][69. Sqrt(x)] 4 Approaches for Finding the Square Root of A Number: Brute Force, Exponent, Binary Search and the Newton Iteration Method
By Long Luo
This article is the solution 4 Approaches: Brute Force, Exponent, Binary Search and the Newton’s Iteration Method of Problem 69. Sqrt(x).
Here shows 4 approaches for finding the square root of a number: Brute Force, Exponent, Binary Search and the Newton’s Iteration Method.
Given an integer \(N\) and a tolerance level \(L\), the task is to find the square root of that number.
Brute Force
The Brute Force way is very easy, just enumerate a value from \(0\) to \(x\), check the product \(i^2\) and target, return the answer.1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17public static int mySqrt(int x) {
if (x == 0 || x == 1) {
return x;
}
for (int i = 0; i < x; i++) {
long sum = i * i;
long bigger = (long) (i + 1) * (i + 1);
if (sum == x) {
return i;
} else if (sum < x && bigger > x) {
return i;
}
}
return 0;
}
Analysis
- Time Complexity: \(O(n)\)
- Space Complexity: \(O(1)\).
Exponent
Noted that:
\[ \sqrt{x} = x^{1/2} = (e ^ {\ln x})^{1/2} = e^{\frac{1}{2} \ln x} \]
So we can use the exponent \(\exp\) and logarithm \(\ln\) to calculate the square root of the number \(\sqrt{x}\).
It’s really a fast and simple way!
Note: Since the computer can’t store the exact value of the float number, and the parameters and return values of the exponential function and logarithmic function are float numbers, so the result may be wrong.
For example, when \(x = 2147395600\), the result of \(e^{\frac{1}{2} \ln x}\) is \(10^{-11}\) from the correct value of \(46340\), so when taking the integer part of the result, you will get the wrong result of \(46339\).
So after getting the integer part \(\textit{ans}\) of the result, we should find out which of \(\textit{ans}\) and \(\textit{ans} + 1\) is the real answer.1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8// Exp O(1) O(1)
public static int mySqrt_exp(int x) {
if (x == 0) {
return 0;
}
int ans = (int) Math.exp(0.5 * Math.log(x));
return (long) (ans + 1) * (ans + 1) <= x ? ans + 1 : ans;
}
Analysis
- Time Complexity: \(O(1)\)
- Space Complexity: \(O(1)\).
Binary Search
We can use Binary Search to solve this problem.
Let the square root of \(x\) is \(k\), \(k^2 \leq x\). The lower bound is \(0\), and the upper bound is \(x\). In each step, we need to compare the middle element \(mid^2 \leq x\) or \(mid^2 > x\), adjust the range of the upper and lower bounds.
Since all our operations are integer operations, there is no error, so after getting the final answer \(\textit{ans}\), there is no need to try \(\textit{ans} + 1\) again.1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18public static int mySqrt_bs_opt(int x) {
if (x <= 1) {
return x;
}
int left = 1;
int right = x / 2;
while (left < right) {
int mid = left + (right - left + 1) / 2;
if (mid > x / mid) {
right = mid - 1;
} else {
left = mid;
}
}
return left;
}
Analysis
- Time Complexity: \(O(\log x)\)
- Space Complexity: \(O(1)\).
Newton’s Method
The Newton’s Method is:
Let \(N\) be any number then the square root of \(N\) can be given by the formula:
\[ root = 0.5 \times (X + (N / X)) \]
where \(X\) is any guess which can be assumed to be \(N\) or \(1\).
- In the above formula, \(X\) is any assumed square root of \(N\) and root is the correct square root of \(N\).
- Tolerance limit is the maximum difference between \(X\) and root allowed.
But how to understand this method?
If we want to find the square root of the integer \(N\). Obviously, the square root of \(N\) is the function \(y = f(x) = x^2 - N\) of zero.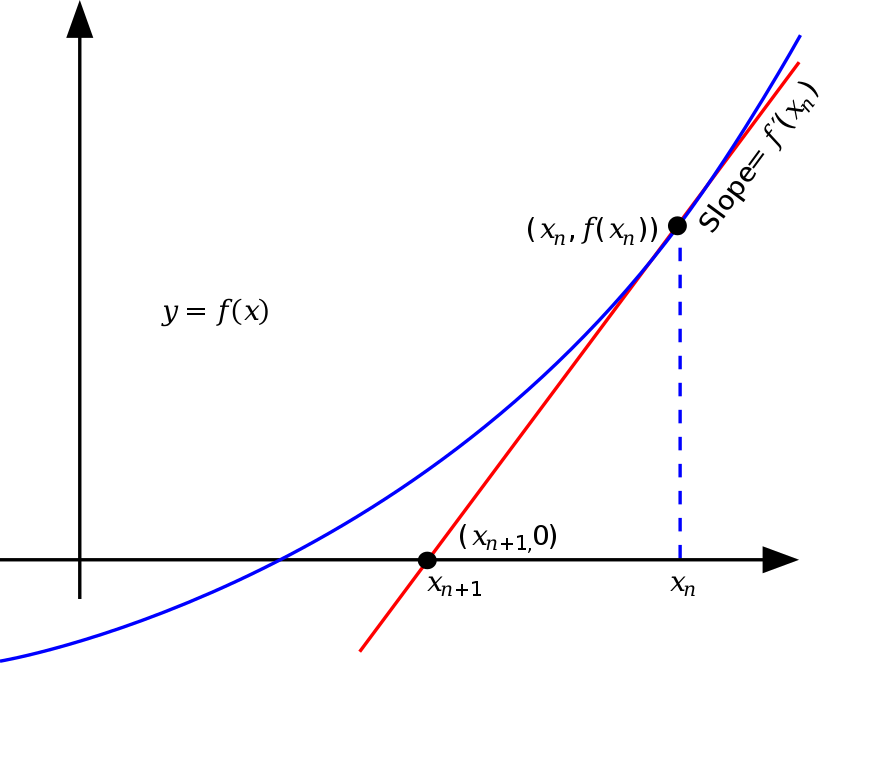
We take any \(x_n\) as an initial value, at each iteration of the step. We find the point \((x_n, f(x_n))\) on the image of the function, make a slope through this point, the derivative of this point \(f'(x_n)\), the intersection with the horizontal axis is denoted as \(x_{n+1}\) compared to \(x_n\). It’s closer to zero.
The equation of the straight line is:
\[ 2 \times x_n = (x_n^2 - N) / (x_n - x) \]
The intersection with the horizontal axis is the equation:
\[ 2 \times x_n \times x - (x_n^2 + N) = 0 \]
which is the new iteration result \(x_{n+1}\):
\[ x_{n+1} = 0.5 \times (x_n + N / x_n) \]
After iterations, the value of the true zero point \(sqrt(N)\) is close enough to be an answer.
There comes two questions: 1. Which initial value do we assign? 2. When does the iteration end?
Initial value
As mentioned rule 1, we assign \(X\) to the \(N\) itself because we want to find the positive \(sqrt(N)\) and \(N\) is surely larger than \(sqrt(N)\).
Ending iteration
After each iteration, the answer is closer to the zero point. So when the intersection obtained from two adjacent iterations is very close, we can conclude that the result at this time is enough for us to get the answer.
As mentioned rule 2, if the calculated root comes inside the tolerance allowed then break out of the loop.
In general, it can be judged whether the difference between the results of two adjacent iterations is less than a very small non-negative number.1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17public static int mySqrt_newton(int x) {
if (x == 0) {
return 0;
}
double N = x;
double x0 = x;
while (true) {
double xi = 0.5 * (x0 + N / x0);
if (Math.abs(x0 - xi) < 1e-7) {
break;
}
x0 = xi;
}
return (int) x0;
}
Analysis
- Time Complexity: \(O(\log x)\)
- Space Complexity: \(O(1)\).
All suggestions are welcome. If you have any query or suggestion please comment below. Please upvote👍 if you like💗 it. Thank you:-)
Explore More Leetcode Solutions. 😉😃💗